INTRODUCTION:
Diabetic foot means a variety of changes which can occur in the foot of diabetic patients. Treatment cost of foot affects the patients financially & hence a lot of research is being done in this area. Diabetic foot is a global problem & it can affect many patients irrespective of race or area of the world. Healthy feet are essential for a good quality of life.
The basic aim of treating this disease is to preserve the normal leg structure & to avoid wound formation & subsequent hospitalization.
STUDY & CONTROL OF DIABETIC FOOT:
Ulcers or long standing non healing wounds in feet are very common in patients having nerve & muscle problems. Diabetes is the major cause of amputation or infected leg removal in patients and people, especially Indians, having uncontrolled diabetes have more chances of amputation than patients with well controlled diabetes.
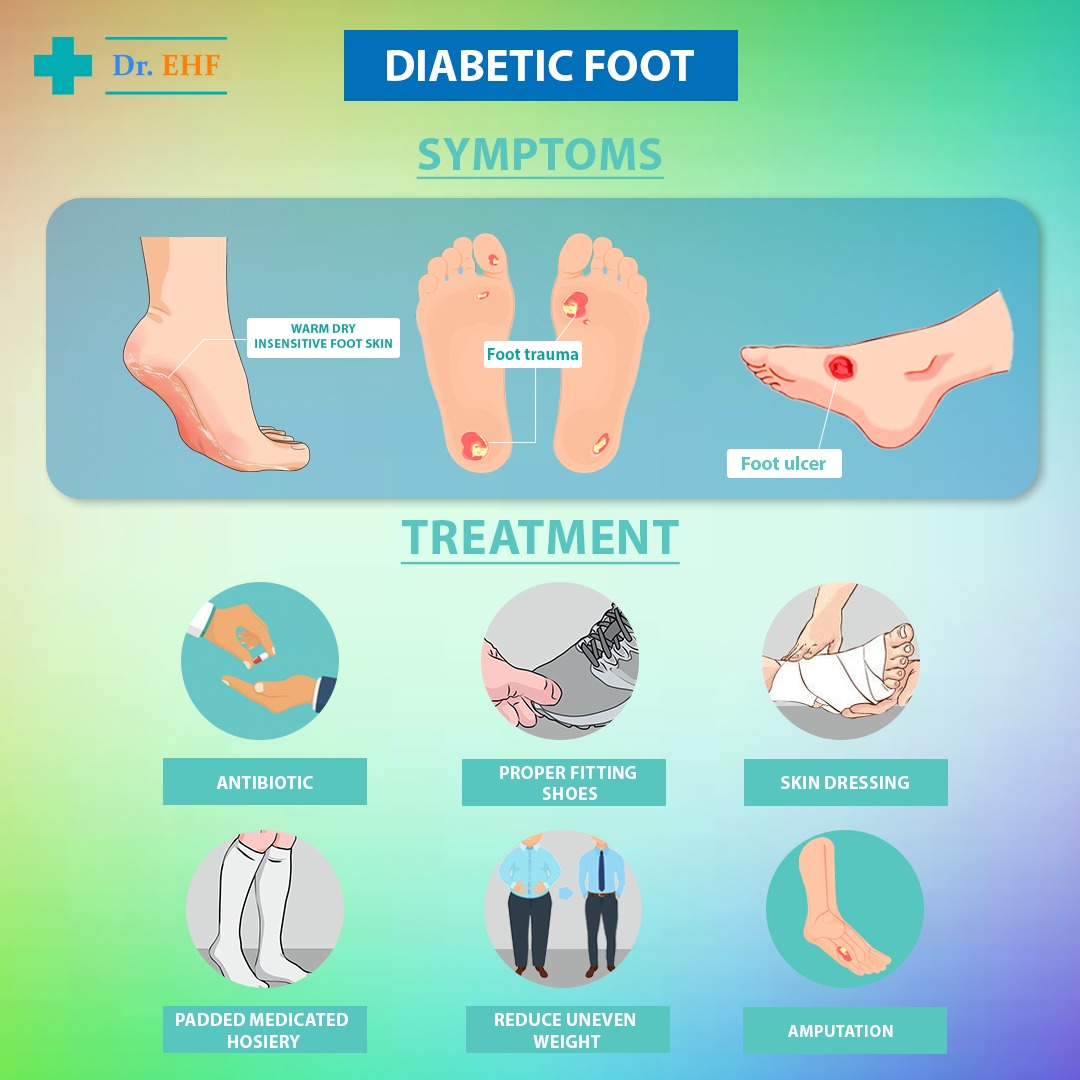
CAUSE OF FOOT WOUNDS IN DIABETICS:
Earlier it was thought that nerve or blood vessel disease was the main cause of diabetic foot but research has now found out that uneven weight put on foot while walking or standing may cause this problem. Nerve disease does speed up this process of wound formation but loss of sensation of pain, pressure and temperature can cause injuries to the patients which could have been avoided. Nerve problems results in increased blood flow to the feet along with dry skin due to nil sweating. Thus, the warm, dry insensitive foot is at high risk of wound which untreated over a period of time becomes an ulcer. Pressure wounds are also formed due to ill-fitting shoes as the sensation of pain is reduced in such patients. It was Dr Paul Brand who stated that pain is ‘God’s greatest gift to man’, and that the loss of pain results in the many disfiguring injuries that patients with conditions such as diabetic neuropathy, leprosy and other long standing nerve related problems experience. Blood vessel disease is well recognized in diabetes and loss of foot pulses may be up to 50% more common in diabetic individuals than in the general population. Rarely, however, is vascular disease alone the only cause of ulceration: more commonly it acts in combination with nerve diseases and conditions such as minor trauma, which lead to increased demands for oxygen and nutrients that the reduced blood circulation cannot meet.
Hence It is a combination of factors mentioned above that results in wounds in diabetic foot though however nerve disease was main cause present in 80 percent of patients with new foot wounds.
MANAGEMENT OF DIABETIC FOOT WOUNDS:
The first thing to do in foot wounds is to reduce pressure on the affected part & then to treat the area with medicines & after it heals, to further prevent its reinfection.
HOW TO OFFLOAD THE DIABETIC FOOT:
To reduce the weight on the foot, it is advised to use wheelchairs, crutches, castings & even bedrest, but patient compliance is a big problem, because in the absence of pain sensation patients overuse the leg without knowing that their feet are being damaged. To be safe patients can use a cast, along with a half shoe, or an air cast boot & it was scientifically found that this helped the wounds to heal faster.
HOW TO MANAGE INFECTIONS:
Controlling wound ulcers in foot is another issue because doctors face antibiotic resistance while treating such patients.
WHICH DRESSING TO USE?
Dressings help to keep the wound clean & healthy, but newer treatments like Bioengineered tissue preparations, growth factors, larvae treatment & antibiotic filled beads are now being tried. For the long-standing infected ulcer with much dead smelly skin or slough in the base, the larvae of the green bottle fly (Lucilia sericata) has been used to good effect. These larvae secrete a number of enzymes that appear to be stop bacteria that cause infection from reproducing; besides they also ingest slough and other infected material. Calcium sulphate beads impregnated with tobramycin have been implanted into localized areas of bone infection or osteomyelitis in the diabetic foot and initial scientific reports suggest potential usefulness of this form of antibiotic management.
Artificial skin grafting is being used & in doing so, it is seen that wound healing is faster by this method. The only drawback of these newer methods are its huge cost.
PREVENTION OF FOOT WOUNDS:
Educating patients with self-care & proper management, including choosing the right pair of shoes which does not cause pain or pressure on the foot. Similarly, protective padded hosiery has been shown in a scientific study to reduce high foot pressures known to be associated with the origin of foot problems Another way to reduce pressure is to inject medicated silicon gel into the foot which helps in reduction of callus or hard skin formation on pressure points & foot ulcer recurrence. This treatment appears to be safe & well tolerated as documented in multiple scientific studies.
CONCLUSION:
Diabetic foot problems are quite common & foot examination must be done in diabetic patients. For a complete checkup of foot, after removing socks & shoes, it is important to examine skin color & shape of fingers & toes. Foot examination can identify high risk patients who may be educated on how to avoid or prevent complications.
The key to healing foot ulcers is weight offloading along with antibiotics, if needed, in proper dressings. Really bad ulcers require antibiotic treatment and new therapies such as growth factors and skin substitutes.
Compiled from various international research journals available at google scholar by D. Mukherjee having 38 years of pharmaceutical (Cardiac, Diabetic, Neurology, Pain & Inflammation products) experience with a Swiss Multinational Company NOVARTIS and edited by Dr Sandeep Ahlawat, MBBS