INTRODUCTION:
We need to work out cost effective screening of breast cancer as it is the most common cancer in the USA and elsewhere. The risk of developing breast cancer in women is increasing steadily, however the silver lining is that screening and early detection has now reduced the death rate to about 25 to 30 percent. The exact cause of breast cancer is not known; however, risk factors like:
1. Strong family history with some near or dear one having it.
2. History of breast biopsy showing cancer growth & changes.
3. Exposure to chest X ray and radiation, but strangely the majority of breast cancer develops in women with no risk factors at all hence the need for cost effective screening tests such as mammography.
MAMMOGRAPHY: -
It is used in two different ways,
1. Screening &
2. Detection or Diagnosis.
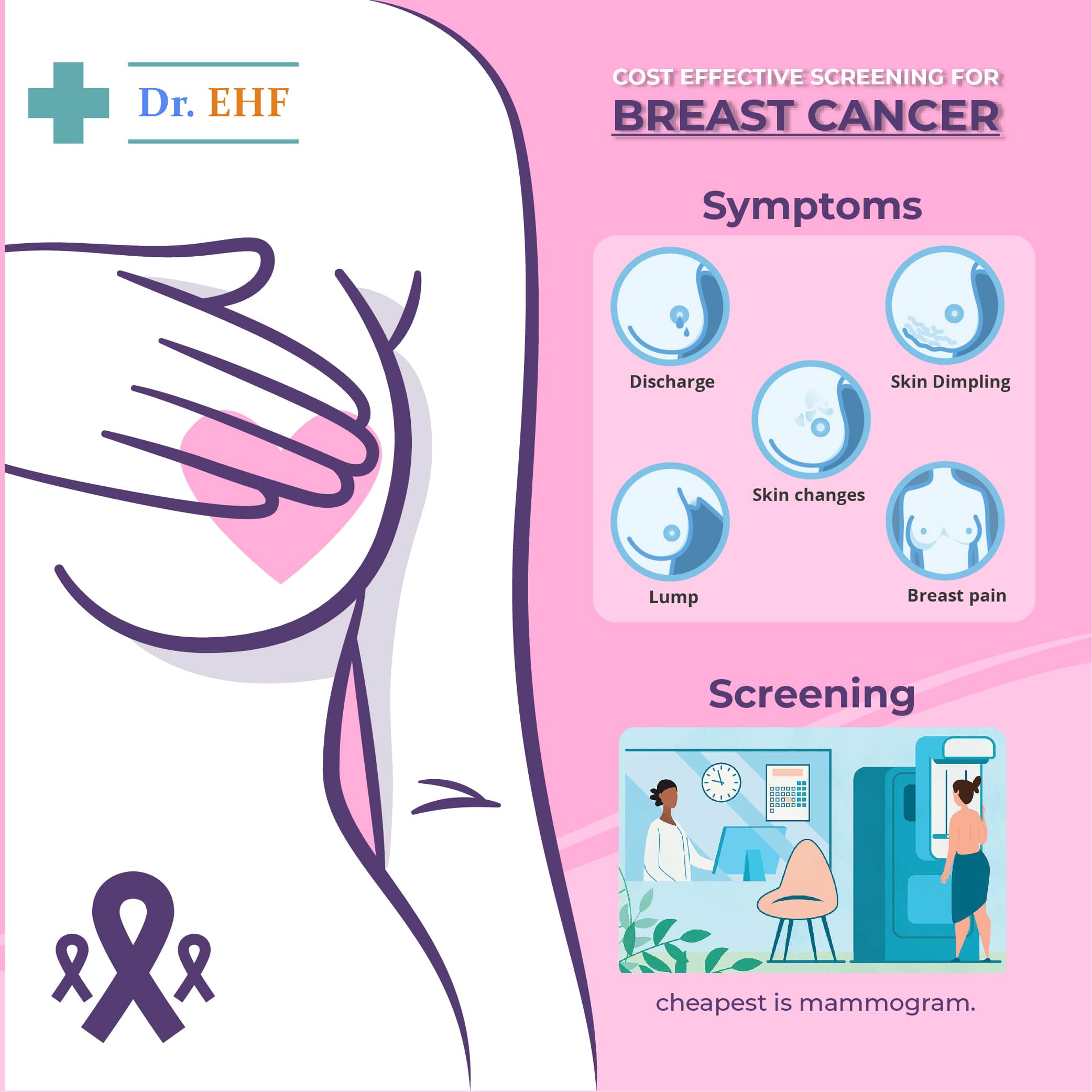
In screening, patients without any symptoms are screened for any abnormalities, eg, Annual mammogram screening camps, etc.
In diagnostic mammography, if a patient is found to have any lump or thickening of tissues or discharge from nipples, dimpling of skin etc. they are further sent for investigation to specific clinics.
Infact diagnostic mammography also includes other methods like Ultrasound (US) , MRI, or Galactography for followup evaluation. Certain standards of evaluation of doing these procedures were laid down & specific trained personnel were only given approval for doing these procedures. Not only the degree of disease was tabulated according to scale, but costs for various tests were also laid down.
SCREENING MAMMOGRAPHY: -
PHYSICIANS AWARENESS: - Screening mammography is very important for all women as per age, because there are unfortunately no earlier signs or known risk factors.
Such guidelines are re-evaluated from time to time by various doctor’s associations, who feel that women above 40 years should be screened at least once a year.
Their recommendations are: -
1. Women whose mother or sister had a known history of breast cancer & are above 40 years of age.
2. Women below 25 years with a hereditary history of breast cancer.
3. Women with biopsy diagnosis or in patients with changes in cells inside mammary glands or ducts.
PATIENT AWARENESS: - Patients normally avoid yearly breast examination due to personal reasons. They can be made to realize that: -
1. The aim of screening is to detect early & treat early.
2. During mammography patients feel only slight discomfort, not pain.
3. Radiation during procedure is within safe limits.
THE LOGISTICS OF MAMMOGRAPHY; WHAT PATIENTS & DOCTORS NEED TO KNOW: -
It would be ideal if the results of mammography are declared on the go as the patients are waiting; because it would be difficult to call them again if results come after the departure of patients from the clinic.
It would also be helpful if patients are advised beforehand that they can be recalled once again, as interpretation of results takes time and involves discussions with other medical specialists. In case patients have earlier reports, these can then be compared with present reports for accuracy in generating reports & treatment.
SUMMARY AND CONCLUSIONS: -
1.The physician should aim to counsel the patient to take screening and then followup on the radiologists advice.
2. The treating doctor should educate the patient on benefits of early detection & early treatment for breast cancer & to convince the patient that the process is painless.
3. Take the patient into confidence regarding the need to sometimes repeat the tests.
Women with breast implants should have their results read very carefully as more tests are needed to be done.
Nowadays Mammographic Computer Aided Detection (CAD) is being used to accurately identify areas of concern in the images taken by the machine. With newer methods being used, the patients " call back " rates have been reduced. Using methods like Digital Mammography is expensive and many times the term " digital " is used as a marketing gimmick.
PHYSICAL EXAMINATION: -
The doctors should be experts in mammography, so that the lump is detected accurately. In younger patients, it should be clearly determined whether the lump is dangerous or not, so that early treatment can be started. Sometimes false negatives, that is there is cancer but the test was unable to detect it, are also reported in 10 to 15 percent of patients, hence patients should be made aware of further tests if need be.
NIPPLE DISCHARGE: -
It is the next most common symptom after lumps & pain & should be treated as:
1. After eliminating pregnancy & hormonal disorders.
2. A mammogram, followed up with relevant followup treatment.
3. A Ductogram is used to identify the affected areas for further surgical treatment.
Pain in the breast can be due to multiple causes, with or without redness. If breast pain is the problem, then treatments are: mammogram, ultrasound, biopsy & mammography by which the disease may be clearly identified.
Breast Implants may also cause rupture of surrounding tissue & cause discomfort.
Surgical procedures include: Needle localization, guided biopsy, core biopsy, vacuum assisted biopsy & ultrasound guidance.
SUMMARY AND CONCLUSIONS:
1. Breast imaging is useful in screening of patients or those who show signs such as lump or pain. This is cheapest to do.
2. Ultrasound is useful in the treatment of breast cancer. This costs slightly more than breast imaging.
3. Needle biopsy below the skin, guided by ultrasound, can be very useful. This involves much higher cost, is risky and troublesome and is done only in very specific cases.
4. Breast MRI, though expensive, is suitable for high-risk patients who cannot undergo needle biopsy for fear of spread of suspected underlying cancer.
Compiled from various international research journals available at google scholar by D. Mukherjee having 38 years of pharmaceutical (Cardiac, Diabetic, Neurology, Pain & Inflammation products) experience with a Swiss Multinational Company NOVARTIS and edited by Dr Sandeep Ahlawat, MBBS